New horizons in 3D printing – get to know PET-G filaments
What is PETG filament?
PETG filament is widely used in 3D printing to produce a variety of objects. PETG, also known as polyethylene glycol terephthalate, is a plastic with many advantages that have made it popular in the 3D printing world.
Learn about the properties of PETG material
PETG filament features:
Strength and flexibility: Unlike PLA, PETG is a material with greater mechanical resistance. It has good strength and ductility, so it is not as brittle. It will perform well in conditions where the ambient temperature does not exceed 60°C.
Ease of printing: PETG is one of the easiest materials to print, compatible with most printers on the market. It can be used to make large parts without the need for an actively heated printer chamber.
Resistance to chemicals: It has good corrosion resistance. This allows it to be used, for example, in situations where the product will come into contact with coolant or isopropyl alcohol.
Wear resistance: If the print will be exposed to abrasion, it is worth considering the choice of PETG. Compared to ABS and even PLA, a product made of PETG should wear out noticeably slower.
Color availability: It is available in a wide range of light-transmitting and non-light-transmitting color varieties. Using the layered structure of the prints, it is possible to make, among other things, lamp shades that diffuse light in a unique way.
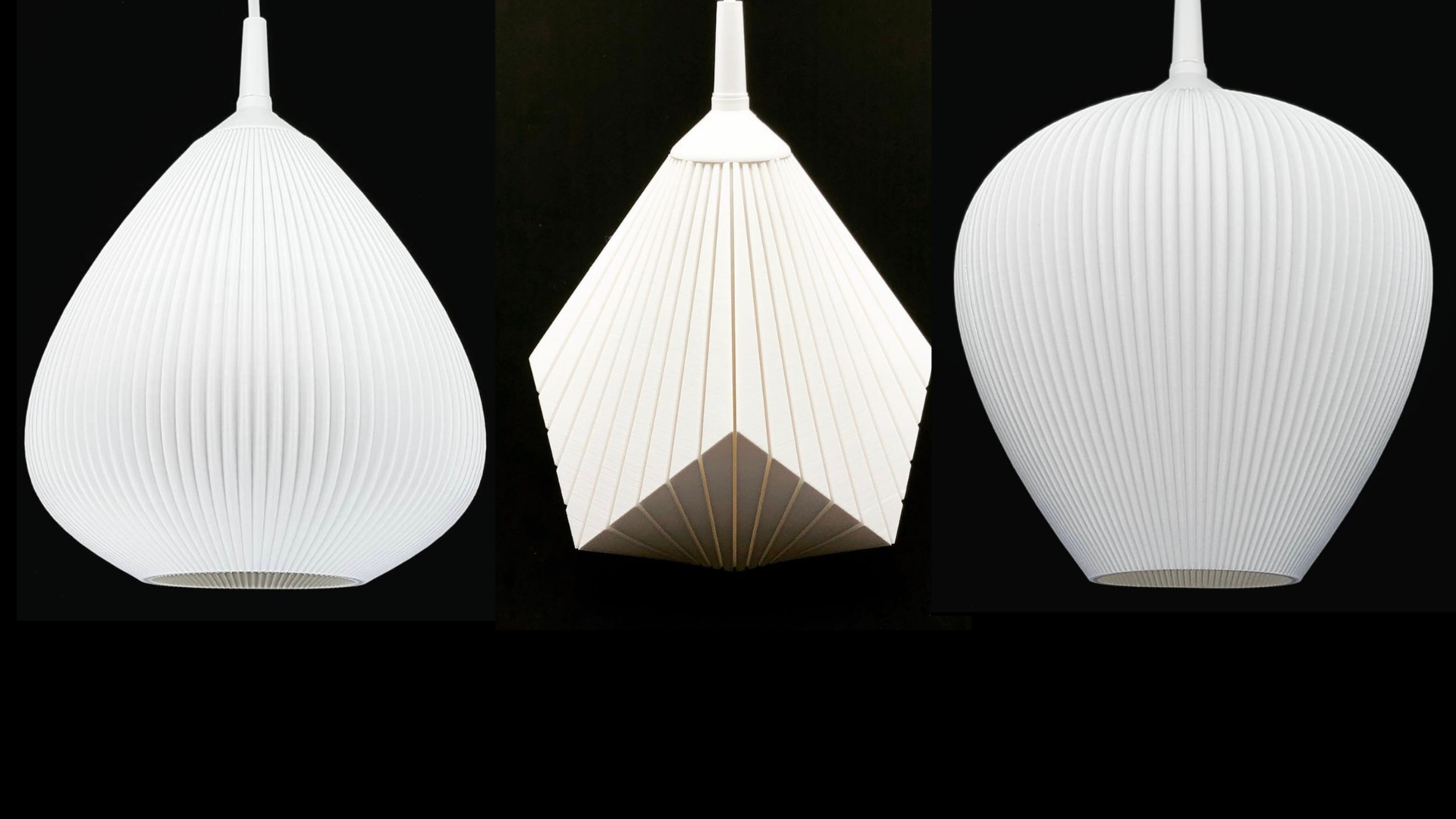 Lampshades made of PETG material
Lampshades made of PETG material
PETG applications:
- Household articles
- Products intended for contact with food (the material must have an appropriate certificate)
- Items exposed to outdoor conditions
One filament manufacturer with a wide range of filaments including PETG is KIMYA.
Kimya PETG-S is a standard PETG filament that meets the requirements of most users. The material is certified for food contact EU 10.2011 and also complies with the REACH regulation and the RoHS directive. Furthermore, the material does not emit any odor during printing.
Those who are looking for a more environmentally friendly solution should use the Kimya PETG-R filament, which is a material that is produced from a minimum of 95% post-industrial recycled PETG.

Kimya PETG-R filament
It is produced from 100% industrial waste sourced from Kimya’s French supplier that initially manufactures thermoforming packaging.
Making 3D parts using the Kimya PETG-R reduces the CO2 impact (climate change) by 30% compared to virgin based Kimya PETG-S (results proven by a Life Cycle Analysis conducted internally).
The material is available in three colours: black, white and natural. The properties of Kimya PETG-R are very similar to those of Kimya PETG-S, despite the fact that it is almost entirely recycled (the natural-coloured material is even 100% recycled!).
Those looking for material for special tasks should look at Kimya PETG Carbon.
This is a material that is a mixture of PETG and chopped carbon fibres, similar to Kimya ABS Carbon or Kimya PEKK Carbon. This combination contributes to reduced shrinkage, increased strength, stiffness and wear resistance.
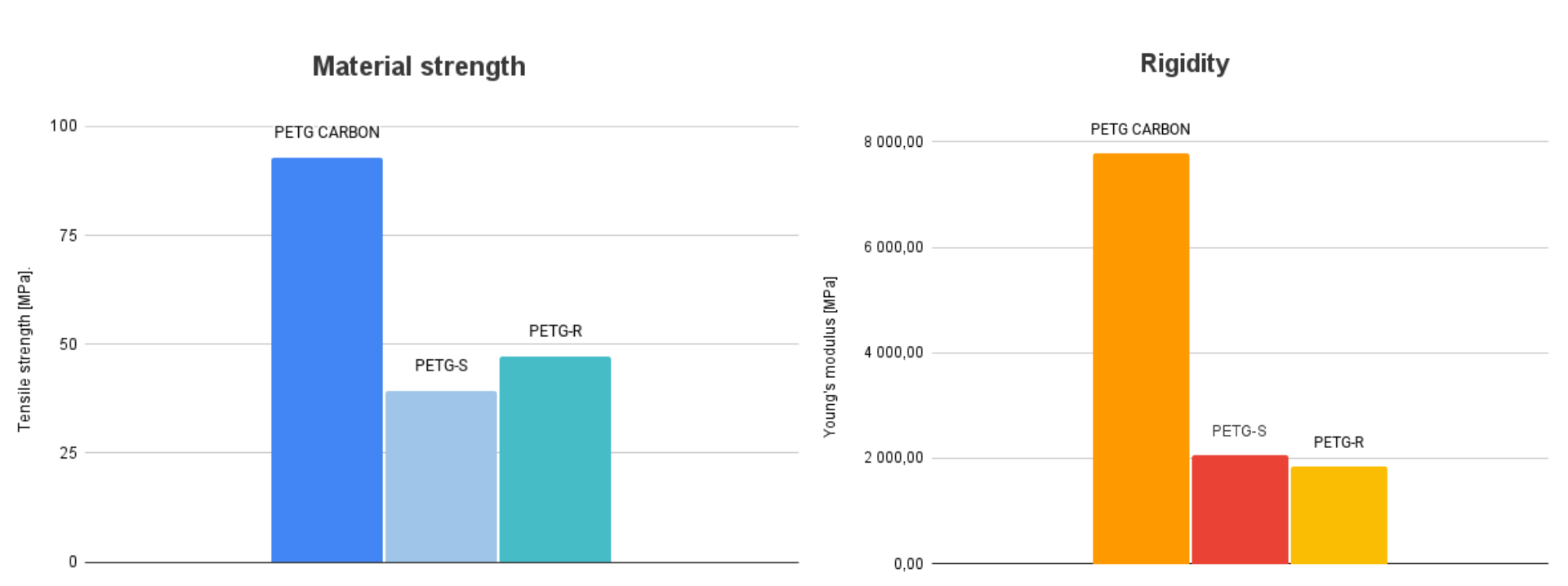
Comparison of the rigidity and material strength of Kimya PETG Carbon with other Kimya PETG materials.
Thanks to its low shrinkage, this filament can be used to make parts requiring high dimensional accuracy. An additional advantage of Kimya PETG Carbon filament is the excellent surface quality of prints made from it. It is worth remembering that it is necessary to use a hardened nozzle made of, for example, hardened steel to print from this material.
The mechanical properties of Kimya PETG Carbon allow it to be used in the medical industry for the production of prostheses, in the engineering sector for the production of instrumentation, and also in the military sector in the context of on-demand production.

Contact:
LinkedIn Wojciech Wiśniewski
e-mail: wwis@omni3d.net
